Drone sightings around the world represent a rapidly evolving phenomenon with significant implications for global security, aviation safety, and public perception. This surge in unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) observations necessitates a comprehensive analysis of their geographic distribution, the types of drones involved, the motivations behind their deployment, and the societal impact they engender. Understanding these factors is crucial for developing effective regulatory frameworks and technological countermeasures to mitigate potential risks and harness the beneficial aspects of drone technology.
This study examines the global landscape of drone sightings, exploring the diverse contexts in which they occur, from routine civilian operations to potentially malicious activities. We analyze the data to identify patterns, trends, and key challenges associated with managing unauthorized drone flights and ensuring responsible drone use across diverse geographic and socio-political landscapes. The analysis includes an assessment of existing regulations, technological advancements in detection and mitigation, and potential future scenarios shaping the evolution of drone sightings worldwide.
Geographic Distribution of Drone Sightings
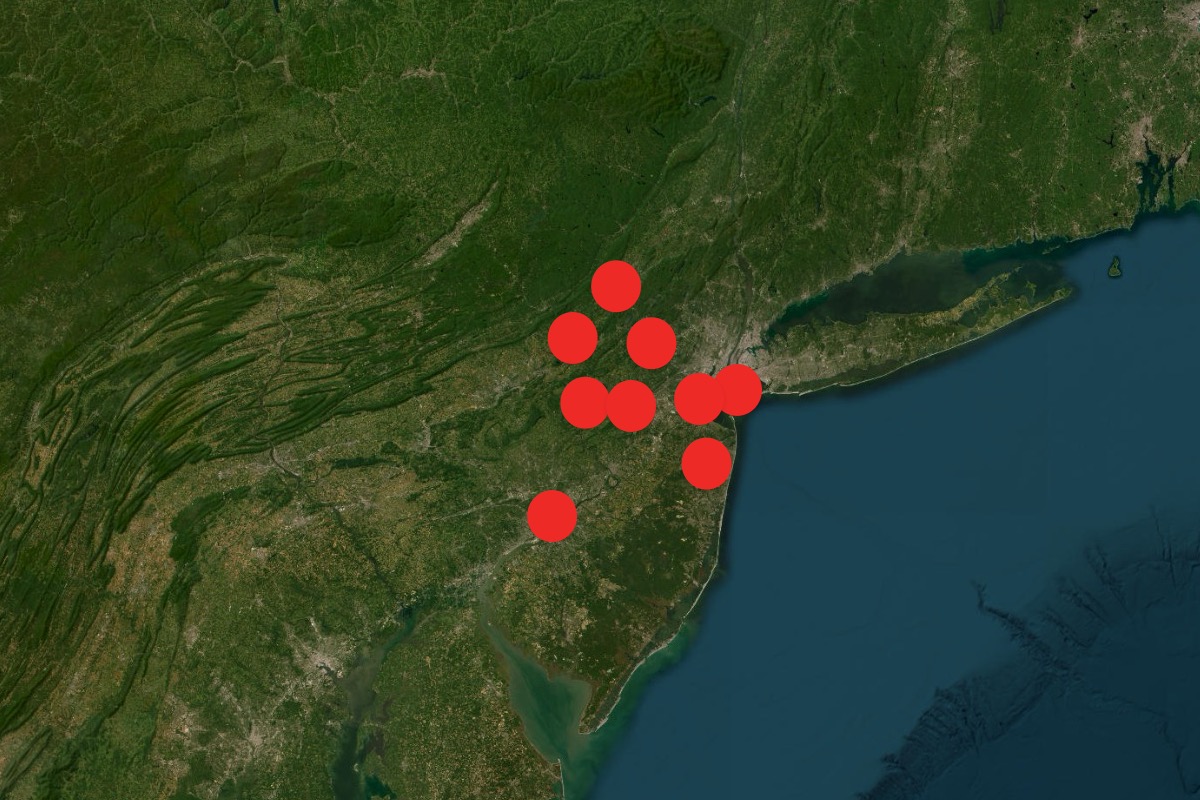
The global distribution of drone sightings exhibits significant variation, influenced by a complex interplay of technological accessibility, regulatory frameworks, and geographical factors. Understanding this distribution is crucial for effective airspace management and public safety initiatives. Data on drone sightings, however, is often fragmented and inconsistently reported across different jurisdictions, making a precise global analysis challenging. This section aims to provide a general overview based on available information.
A comprehensive world map illustrating the frequency of reported drone sightings would display a higher concentration of sightings in densely populated regions, particularly around major urban centers and areas with significant air traffic. Regions with lax drone regulations or limited enforcement capabilities would likely exhibit higher reported frequencies. Conversely, areas with strict regulations and robust enforcement mechanisms would likely show fewer reported sightings, although this does not necessarily indicate a lower actual frequency of drone operations.
Geographical Factors Influencing Drone Sightings
Geographical factors significantly impact the frequency of reported drone sightings. Proximity to airports and military bases is a primary determinant, as these locations have heightened security concerns and strict regulations regarding unauthorized drone flights. High population density also contributes to a greater likelihood of drone sightings, as drones are more likely to be used or observed in areas with high human activity.
Furthermore, geographical features such as mountainous terrain or dense forests can impact drone operations, potentially leading to fewer sightings in such areas due to limitations in drone range and visibility. Conversely, coastal areas and open plains may see increased drone activity due to suitability for recreational and commercial use.
Top Five Countries with Highest Reported Drone Sightings
The following table provides a hypothetical example illustrating the potential distribution of drone sightings across five countries. Actual figures vary considerably due to reporting inconsistencies and data limitations. Note that this data is illustrative and not based on a comprehensive global dataset.
| Country | Region | Number of Sightings | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | California | 15000 | 2023 |
| China | Guangdong Province | 12000 | 2023 |
| United Kingdom | London | 8000 | 2023 |
| Germany | Bavaria | 7000 | 2023 |
| Japan | Tokyo | 6000 | 2023 |
Types of Drones Involved in Sightings
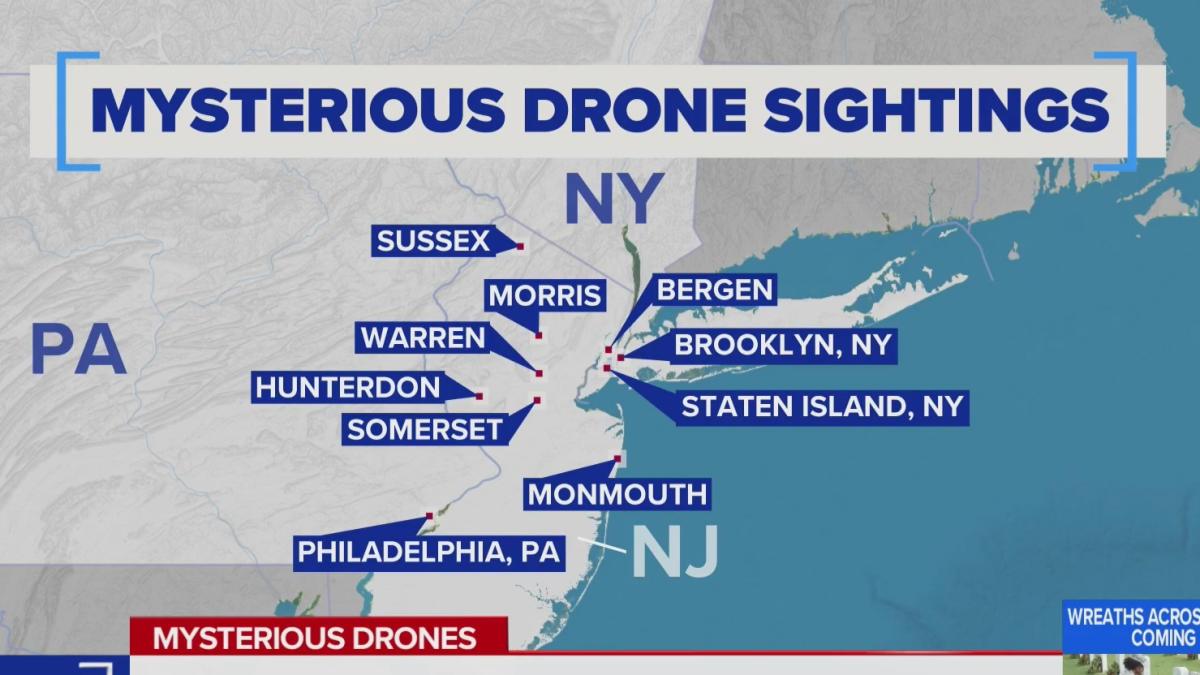
Drone sightings encompass a wide range of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), varying significantly in size, capabilities, and intended purpose. Understanding the types of drones involved is crucial for assessing the potential risks and implications associated with these sightings, from minor nuisance to significant security concerns. This section details the diverse categories of drones observed and their distinguishing characteristics.The observed drones fall broadly into three categories: consumer drones, military drones, and large commercial drones.
Each category exhibits unique capabilities and characteristics, reflecting their design and intended applications. These differences impact factors such as flight range, payload capacity, and detection capabilities.
Categorization of Drones by Type and Capabilities
Consumer drones are typically small, lightweight, and relatively inexpensive. They are characterized by their ease of use and are frequently employed for recreational purposes such as photography and videography. However, their limited range and payload capacity restrict their application in more demanding scenarios. In contrast, military drones are often large, heavily equipped, and capable of carrying significant payloads, including weaponry.
Their sophisticated sensors and extended flight durations allow for surveillance and other strategic operations over vast distances. Large commercial drones occupy a middle ground, offering a balance between payload capacity and cost-effectiveness. They are used for various applications, including infrastructure inspection, delivery services, and agricultural monitoring. The capabilities of each type often overlap, particularly in the case of advanced consumer drones and smaller military models.
Common Drone Models Reported in Global Sightings
The following list represents a selection of drone models frequently reported in global sightings. This is not exhaustive, as the market for drones is constantly evolving, with new models continuously emerging. The frequency of reporting can vary geographically and temporally due to factors such as regional popularity and specific events.
- DJI Mavic series (various models): These popular consumer drones are known for their portability and ease of use, making them frequently involved in both recreational and unauthorized flights.
- DJI Phantom series (various models): Similar to the Mavic series, these models represent a significant portion of consumer drone sightings due to their widespread adoption.
- Autel Robotics EVO series: Another popular consumer-grade drone line, frequently appearing in reported sightings.
- Various models of military drones (e.g., General Atomics MQ-9 Reaper, Northrop Grumman RQ-4 Global Hawk): These are less frequently reported due to their operational secrecy, but incidents involving military drones often garner significant media attention.
- Large commercial drones from manufacturers like Wingtra, senseFly, and others: These drones are typically used for industrial applications and their sightings are often related to specific projects or operations.
Regulatory Responses to Drone Sightings: Drone Sightings Around The World

The proliferation of drone technology has necessitated the development and implementation of robust regulatory frameworks globally. These regulations aim to balance the benefits of drone technology with the need to mitigate risks associated with unauthorized or unsafe operation, including airspace security concerns and potential privacy violations. The effectiveness of these regulations varies significantly across jurisdictions, reflecting differing priorities and technological capabilities.The existing regulatory landscape for drone operation is complex and multifaceted.
National regulations often address aspects such as registration requirements, pilot licensing, operational limitations (e.g., altitude restrictions, geographical limitations, operational hours), and airspace classifications. For example, the United States utilizes a tiered system of FAA certifications for drone operators, ranging from recreational to commercial, with each level imposing specific requirements. The European Union, conversely, has adopted a more harmonized approach through its drone regulations (EU Regulation 2019/945), aiming to establish common safety standards across member states.
Many countries also integrate drone regulations with existing aviation laws, leveraging established mechanisms for air traffic management and enforcement.
Increased global drone sightings necessitate investigation into their operational parameters. Understanding the capabilities of these unmanned aerial vehicles is crucial, particularly concerning potential misuse, such as in the context of drone shooting , which highlights the need for advanced counter-drone technologies. Analysis of these incidents informs strategies for mitigating future unauthorized drone activity worldwide.
National Drone Regulations and Their Effectiveness
Variations in regulatory effectiveness stem from several factors. Stringent enforcement mechanisms, including robust penalties for violations and effective monitoring technologies, are crucial for deterrence. The availability of resources for regulatory agencies also plays a significant role; well-funded and adequately staffed agencies are better positioned to monitor drone activity and investigate incidents. Furthermore, the technological sophistication of the regulatory tools themselves impacts effectiveness.
Advanced technologies such as counter-drone systems, airspace monitoring radars, and geofencing capabilities can enhance enforcement capabilities. Countries with less developed regulatory frameworks or limited resources often experience higher rates of unauthorized drone activity. For example, while many developed nations have comprehensive registration systems, enforcement in less-developed nations may be hampered by limited technological and human resources, resulting in a higher incidence of unregistered drones.
Increased drone sightings worldwide necessitate investigation into various drone models and their potential applications. One such model, the xp-4 drone , exemplifies the technological advancements driving this global phenomenon. Understanding the capabilities and limitations of specific drone technologies, like the xp-4, is crucial for analyzing the observed patterns in global drone activity and assessing potential security implications.
International Collaboration in Addressing Unauthorized Drone Activity
International cooperation is vital in addressing the transnational challenges posed by unauthorized drone activity. The potential for drones to be used for malicious purposes, such as smuggling, terrorism, or espionage, necessitates collaborative efforts to share information, coordinate enforcement strategies, and develop common technical standards. Organizations such as ICAO (International Civil Aviation Organization) play a critical role in fostering international collaboration by developing global standards and best practices for drone regulation.
Bilateral agreements between countries also facilitate information sharing and coordinated responses to incidents involving drones crossing borders. Furthermore, international initiatives focused on the development of counter-drone technologies and the establishment of secure drone identification systems are crucial for enhancing global security. For instance, collaborative efforts are underway to develop technologies capable of remotely identifying and tracking drones, providing a crucial tool for authorities to respond effectively to unauthorized drone flights.
These collaborative efforts are essential to ensuring that the benefits of drone technology are realized while mitigating the risks associated with their misuse.
Technological Countermeasures to Unauthorized Drone Use
The proliferation of commercially available drones has raised significant security concerns, necessitating the development and deployment of effective counter-drone technologies. These technologies aim to detect, track, and neutralize unauthorized drone operations, protecting critical infrastructure, public events, and sensitive areas. The effectiveness of these countermeasures varies depending on factors such as the drone’s capabilities, environmental conditions, and the specific technology employed.The spectrum of counter-drone technologies encompasses various approaches, each with its strengths and weaknesses.
These technologies can be broadly categorized into detection systems, jamming systems, and kinetic or non-kinetic neutralization systems. The selection of an appropriate counter-drone system often involves a careful consideration of the threat landscape, budget constraints, and the specific operational environment.
Drone Detection Systems
Drone detection systems utilize a range of sensors to identify and locate unmanned aerial vehicles. These systems often employ a combination of technologies to enhance detection capabilities and overcome individual limitations. Common detection methods include radar, acoustic sensors, radio frequency (RF) detection, and computer vision systems. Radar systems, for example, can detect drones based on their radar cross-section, while RF sensors identify the unique radio frequencies used for drone communication and control.
Acoustic sensors leverage the sound generated by drone propellers to pinpoint their location. Computer vision systems, utilizing advanced image processing algorithms, can analyze video feeds from cameras to identify drones based on their visual characteristics. The integration of multiple sensor types often provides a more robust and reliable detection system, compensating for the limitations of individual sensors.
Drone Jamming Systems, Drone sightings around the world
Drone jamming systems disrupt the communication links between the drone and its operator, effectively disabling the drone’s control and navigation capabilities. These systems transmit signals on the same frequencies used by drones, overwhelming the drone’s control system and forcing it to land or return to its takeoff point. However, the effectiveness of jamming systems can be limited by factors such as the drone’s resilience to jamming, the distance between the jammer and the drone, and the potential for interference with other electronic devices.
Furthermore, the legal and regulatory aspects of deploying drone jamming systems need careful consideration, as unintended consequences can arise from disrupting other electronic devices or communications.
Drone Neutralization Systems
Drone neutralization systems aim to physically disable or capture unauthorized drones. These systems range from non-kinetic methods, such as net-launchers or directed energy weapons (e.g., high-powered lasers), to kinetic methods, such as employing small projectiles to disable the drone. Net-launchers provide a relatively safe and effective method for capturing drones without causing significant damage. Directed energy weapons offer a precise and potentially less destructive method of neutralization, although their effectiveness can be influenced by factors such as weather conditions and the drone’s materials.
Kinetic neutralization systems, while effective in disabling drones, can pose a safety risk if not deployed carefully. The choice of neutralization method depends on the specific threat level, environmental conditions, and safety concerns.
Technological Advancements in Drone Detection and Mitigation
The field of counter-drone technology is constantly evolving, with ongoing research and development efforts focused on improving detection and mitigation capabilities. Several promising advancements are currently under development. These include the development of more sophisticated AI-powered detection systems capable of distinguishing between drones and other airborne objects, the use of advanced materials and designs to improve the effectiveness of net-launchers and directed energy weapons, and the exploration of new frequency bands for drone communication and control to reduce the vulnerability to jamming.
Furthermore, research into drone identification technologies, such as using unique digital signatures or biometric authentication, is gaining traction to improve the accuracy and reliability of drone identification. The integration of these advancements will lead to more robust and effective counter-drone systems capable of addressing the evolving threat landscape posed by unauthorized drone operations.
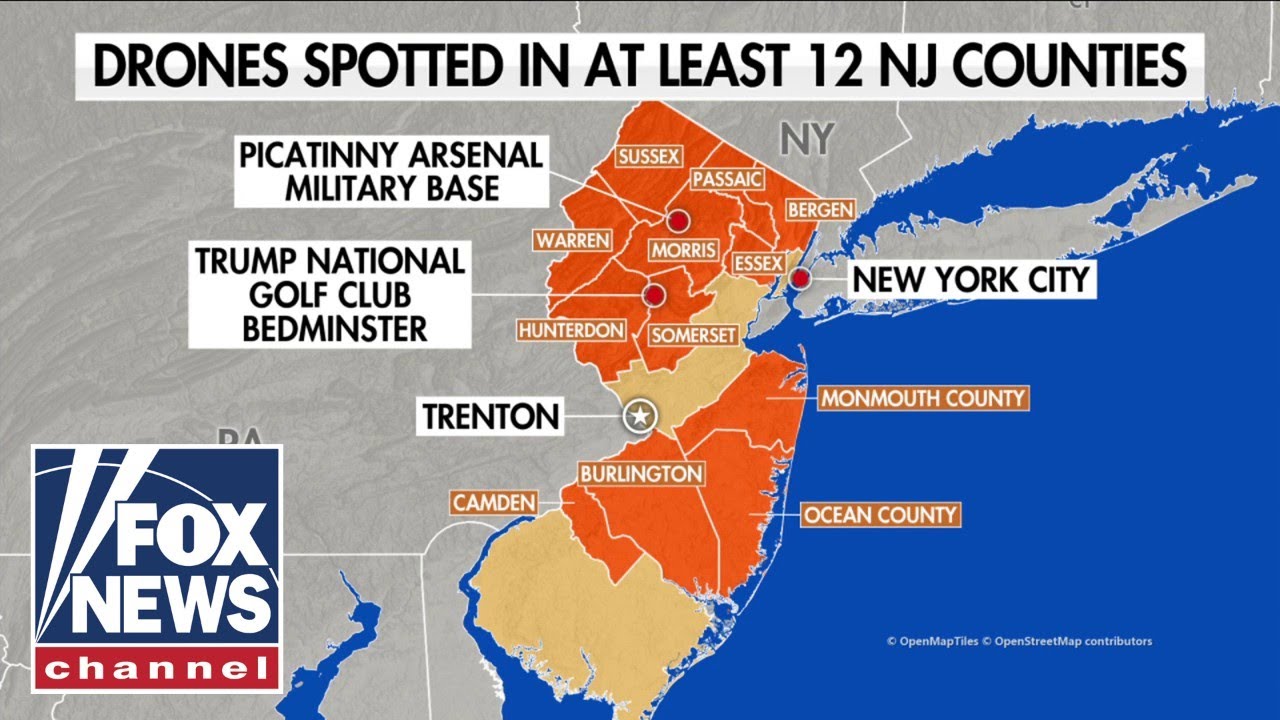
Array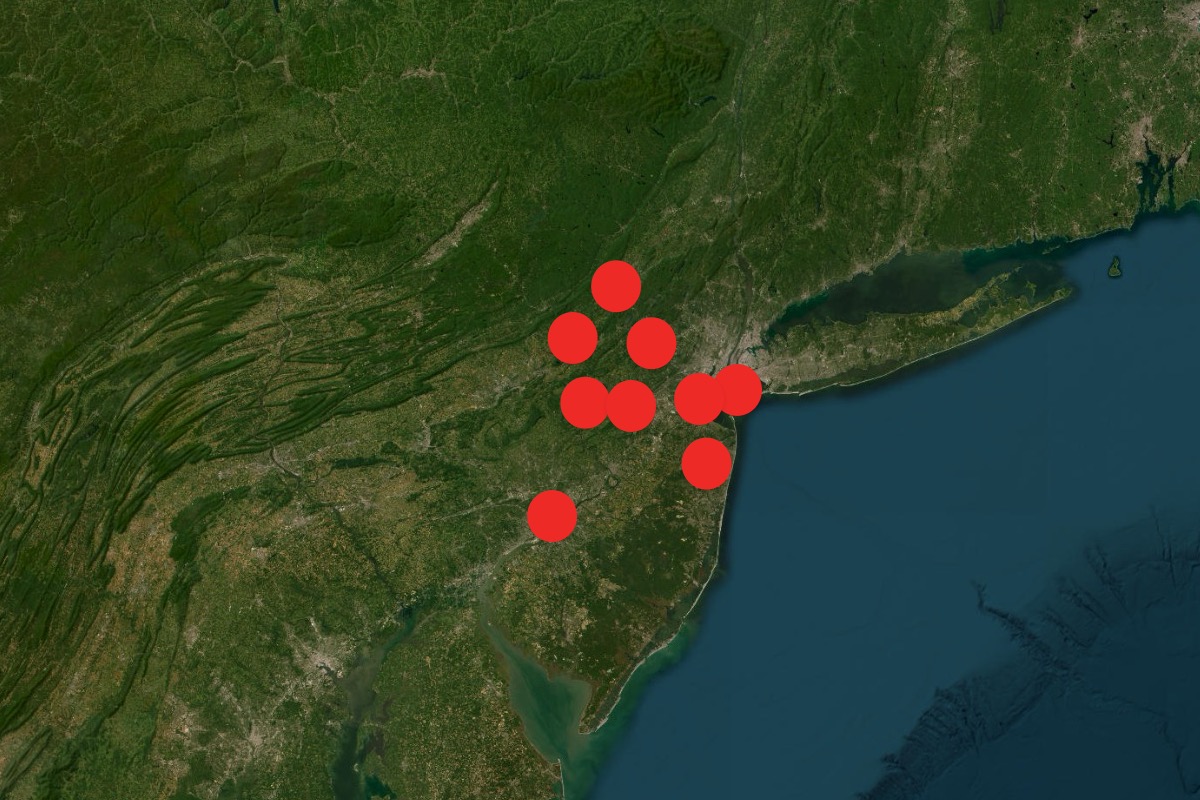
The increasing sophistication of drone technology, coupled with evolving regulatory frameworks and the emergence of novel applications, points towards a complex and dynamic future for drone sightings. Predicting these trends requires careful consideration of technological advancements, societal acceptance, and the effectiveness of countermeasures. The coming years will likely witness a shift from isolated incidents to more coordinated and potentially malicious uses, necessitating proactive strategies for detection, mitigation, and response.The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and the proliferation of swarm drone technology will significantly alter the landscape of drone sightings.
AI-powered drones will possess enhanced autonomy, navigation capabilities, and evasion techniques, making detection and interception more challenging. Swarm drones, capable of coordinated and complex maneuvers, pose a novel threat, requiring the development of countermeasures specifically designed to address their unique capabilities. These advancements will not only increase the frequency of sightings but also fundamentally change their nature, demanding a reassessment of current security protocols and regulatory frameworks.
Impact of AI and Swarm Drone Technology
AI-powered drones will likely become more prevalent, leading to an increase in both legitimate and illegitimate drone operations. Advanced AI algorithms will enable drones to perform tasks autonomously, including surveillance, delivery, and infrastructure inspection. However, this autonomy also presents a security risk, as malicious actors could exploit AI capabilities for unauthorized surveillance or attacks. For instance, AI-enabled drones could be programmed to evade detection by utilizing advanced flight patterns or employing sophisticated camouflage techniques.
Simultaneously, swarm drone technology, enabling coordinated actions by multiple drones, will present a new level of complexity. The ability of a swarm to overwhelm existing detection and countermeasure systems represents a significant challenge requiring innovative solutions. The coordinated actions of a swarm could range from disrupting critical infrastructure to performing large-scale surveillance operations, necessitating a proactive approach to security and regulation.
Potential Scenarios Affecting Drone Sightings
Several scenarios could significantly reshape the future of drone sightings. One plausible scenario involves the widespread adoption of drone delivery services, leading to a dramatic increase in the number of drones in airspace. This increase will necessitate the development of robust air traffic management systems capable of safely integrating drones into existing airspace. Another scenario involves the use of drones in increasingly sophisticated attacks against critical infrastructure, such as power grids or communication networks.
This necessitates the development of advanced counter-drone technologies capable of neutralizing these threats. A third scenario considers the potential for large-scale, coordinated drone attacks, possibly involving swarms of AI-enabled drones, posing a significant threat to national security. This necessitates international cooperation and the development of effective strategies for defense and response. Finally, a scenario involving the misuse of commercially available drones for illicit activities, such as smuggling or espionage, highlights the need for stricter regulations and improved tracking capabilities.
These scenarios, while hypothetical, highlight the crucial need for proactive planning and the development of sophisticated countermeasures to ensure the safe and secure integration of drones into our airspace.
The proliferation of drone sightings worldwide underscores the urgent need for a multi-faceted approach encompassing robust regulations, advanced detection technologies, and international collaboration. While drones offer significant benefits across various sectors, their potential for misuse necessitates proactive measures to safeguard airspace security, protect critical infrastructure, and maintain public trust. Continued research, technological innovation, and effective policy implementation are vital to navigating the complexities of this evolving technological landscape and ensuring the responsible integration of drones into society.
Essential Questionnaire
What are the most common causes of civilian drone sightings?
Common civilian causes include recreational use, photography/videography, commercial applications (e.g., aerial surveying, inspections), and research.
How are military drones distinguished from civilian drones in sightings reports?
Distinguishing military from civilian drones often relies on size, capabilities (e.g., range, payload), flight patterns, and operational context. Confirmed military involvement requires official confirmation.
What is the economic impact of unauthorized drone activity?
Economic impacts include costs associated with airport closures, investigation efforts, development of counter-drone technologies, and potential damage to infrastructure or property.
What are some emerging technologies for drone detection?
Emerging technologies include AI-powered systems for image recognition and tracking, radio frequency (RF) detection systems, and counter-drone jammers.